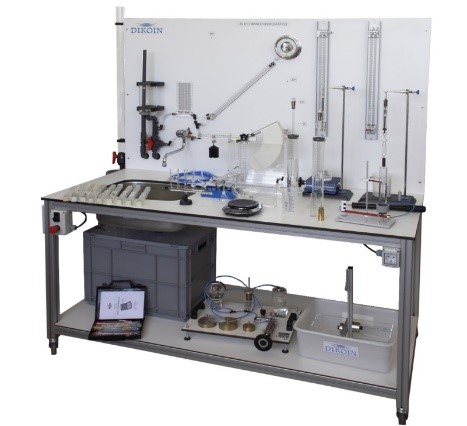
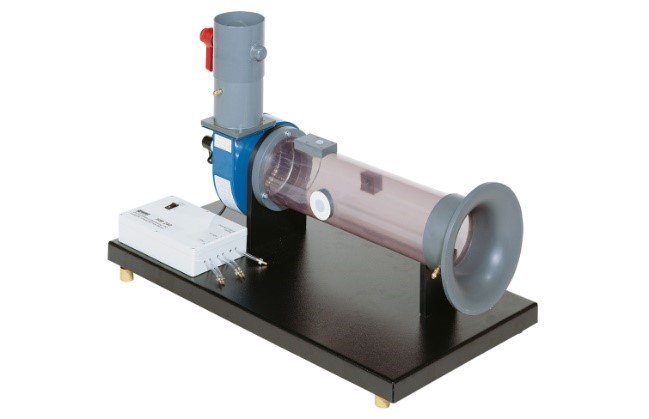
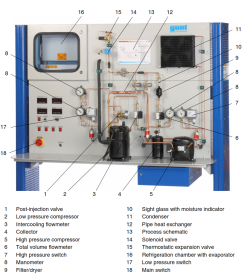
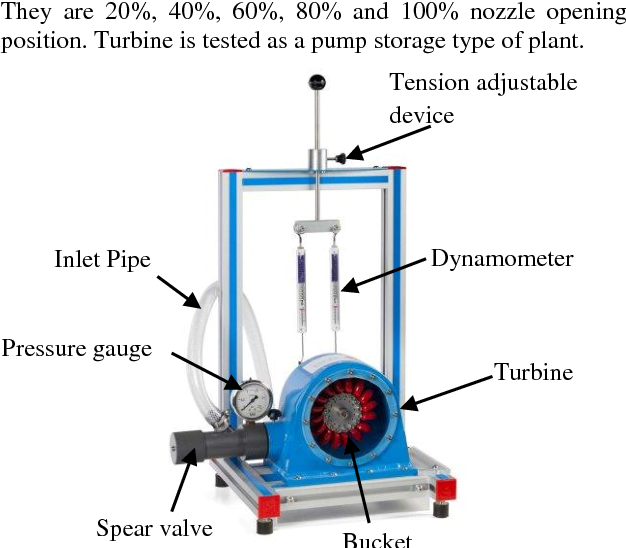
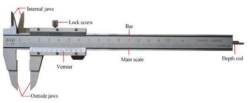
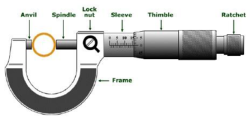
Determine the performance of different types of pumps by calculating: 1.Determination of the Q curve vs rpm. of a centrifugal, a peripheral, a gear, and an axial pump. 2. Determination of the curve H vs Q for different rpm. of a centrifugal, a peripheral, a gear, and an axial pump. 3.Determination of the mechanical power vs flow for different rpm. of a centrifugal, a peripheral, a gear, and an axial pump. 4. Determination of the curve vs the flow for different rpm. of a centrifugal, a peripheral, a gear, and an axial pump. 5.Determination of the map of a centrifugal, a peripheral, a gear, and an axial pump. 6 Determination of a dimensional characteristic curves for different types of pumps. 7. Determination of the specific speed of different types of pumps. |